Role Of Soil Enzymes In Soil Disease Control
Role of soil enzymes in soil disease control. Soil enzymes play a vital role in initiating and maintaining the biogeochemical cycles of these nutrients and provide the basic support of fertility for the healthy development of plants Fang et al 2010. Abstract Soil enzymes play a key role in the energy transfer through decomposition of soil organic matter and nutrient cycling and hence play an important role in agriculture. β-amylase This enzyme is widely distributed in plants and soils so it plays a significant role in the.
The environmental conditions can vary widely. Enzymes respond to soil management changes long before other soil quality indicator changes are detectable. Dick et al 1996.
Soil enzymes are constantly playing vital roles for the maintenance of soil ecology and soil health. Some pathogens favor damp conditions some like certain soil pH. In addition an efficient extraction procedure for immobilised enzymes in soil should avoid the lysis of microbial cells and thus the consequent release of intracellular enzymes the formation of artefacts during soil.
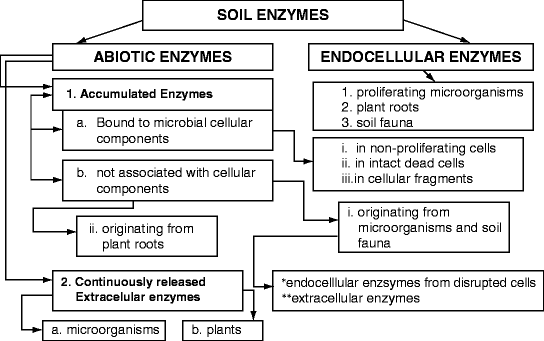
When calculated on the basis of organic matter forest soils showed higher enzyme activities than agricultural soils and enzymes showed higher potential activity around alders than. Soil enzymes play an important role in organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling see Table 187. These enzymatic activities in the soil are mainly of microbial origin being derived from intracellular cell-associated or free enzymes.
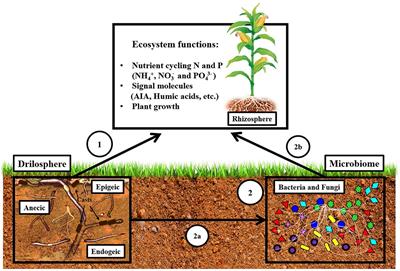
ENZYMATIC REACTIONS AND IMPACT In soil ecosystems the enzymes play vital role on ON FERTILITY carbon nitrogen sulfur and other nutrients cycles The soil hosts plants and animal organisms and also it Tabatabai and Dick 2002. Activity is influenced by physico- chemical properties on soil enzyme. This enhanced enzyme activities slightly compared to chemical fertilizers but the effect was not consistent.
These enzymatic activities in the soil are mainly of microbial origin being derived from. In the case of soil-borne diseases the pathogens can remain in the soil for long periods waiting for the host - our plants - to come along. According to Burns 1982 enzymes entrapped by humic colloids are essential for the successful competition of microbial cells in the hostile soil extracellular environment.
Identification of soils 3. Soil enzymes are constantly playing vital roles for the maintenance of soil ecology and soil health.
Some pathogens favor damp conditions some like certain soil pH.
Other nutrients are acquired in mineral form from the soil. Thus they provide a useful tool to long-term monitor the changes in soil. Enzymes respond to soil management changes long before other soil quality indicator changes are detectable. Soil enzymes are constantly playing vital roles for the maintenance of soil ecology and soil health. Some pathogens favor damp conditions some like certain soil pH. Soil enzymes play an important role in organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling see Table 187. Abstract Soil enzymes play a key role in the energy transfer through decomposition of soil organic matter and nutrient cycling and hence play an important role in agriculture. In addition an efficient extraction procedure for immobilised enzymes in soil should avoid the lysis of microbial cells and thus the consequent release of intracellular enzymes the formation of artefacts during soil. When calculated on the basis of organic matter forest soils showed higher enzyme activities than agricultural soils and enzymes showed higher potential activity around alders than.
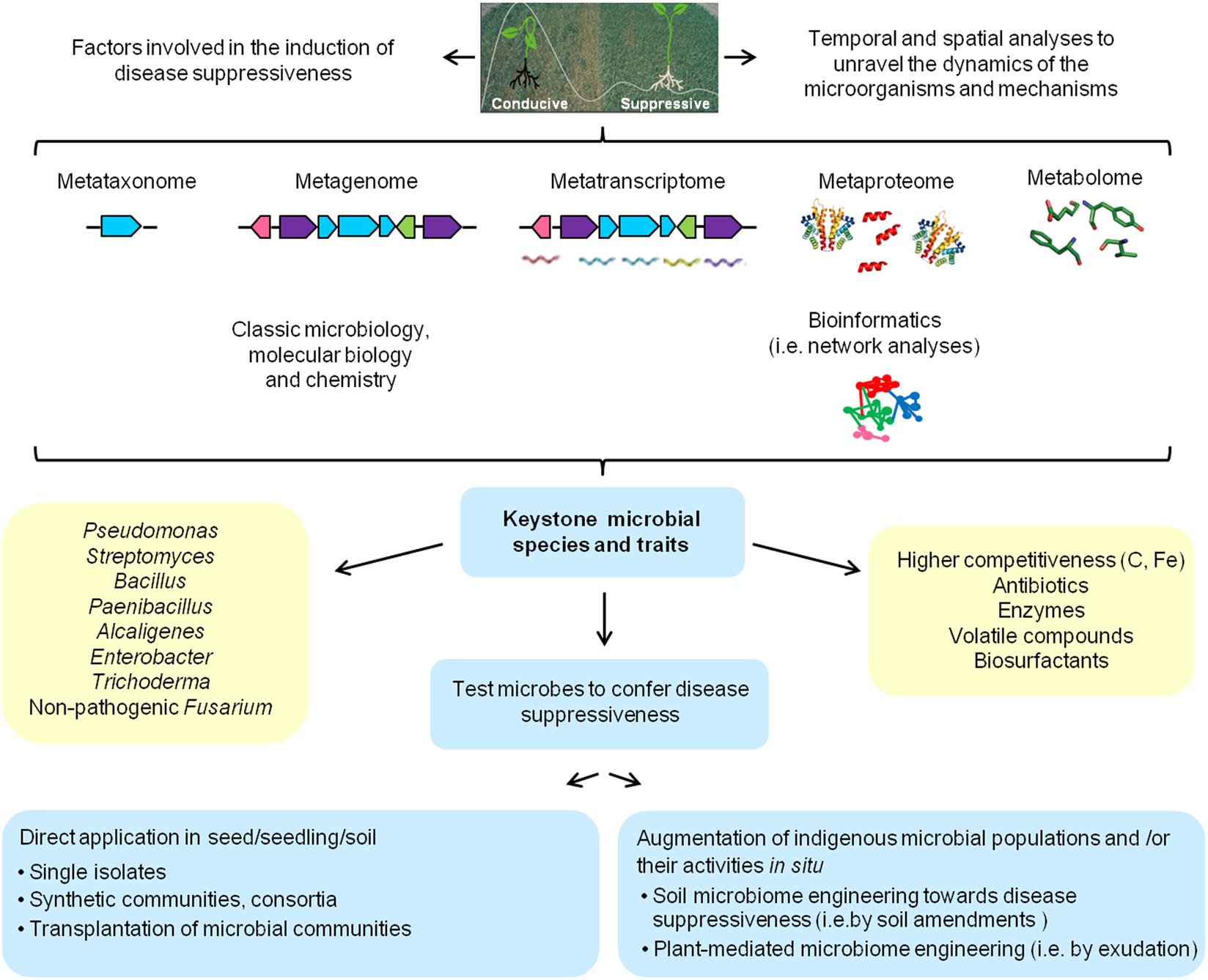
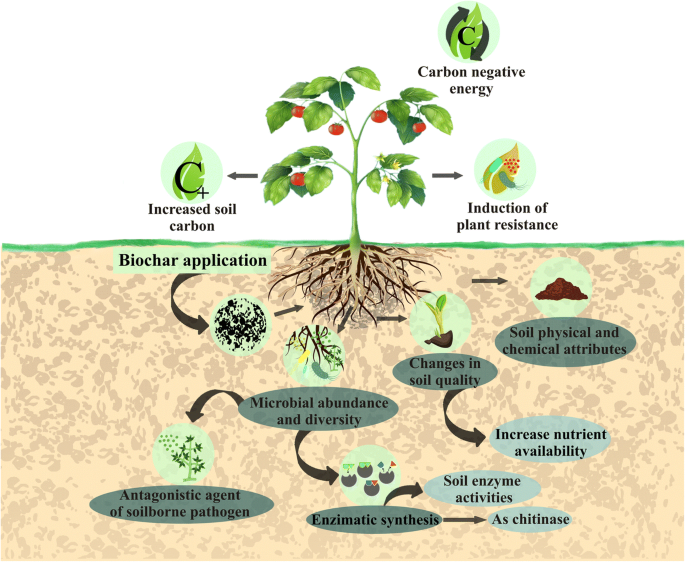
Thus they provide a useful tool to long-term monitor the changes in soil. In recent decades several researches have shown the potential of application of vermicompost in controlling soil-borne plant fungal diseases. Importance of Soil Enzymes 1. Other nutrients are acquired in mineral form from the soil. Particularly the stabilised enzymes can catalyse the transformation of high molecular substrates into products that can be taken up by near microbial cells and can act as inducers or chemoattrac-tants. According to Burns 1982 enzymes entrapped by humic colloids are essential for the successful competition of microbial cells in the hostile soil extracellular environment. In addition an efficient extraction procedure for immobilised enzymes in soil should avoid the lysis of microbial cells and thus the consequent release of intracellular enzymes the formation of artefacts during soil.


























Post a Comment for "Role Of Soil Enzymes In Soil Disease Control"