Is Asthma An Inflammatory Disease
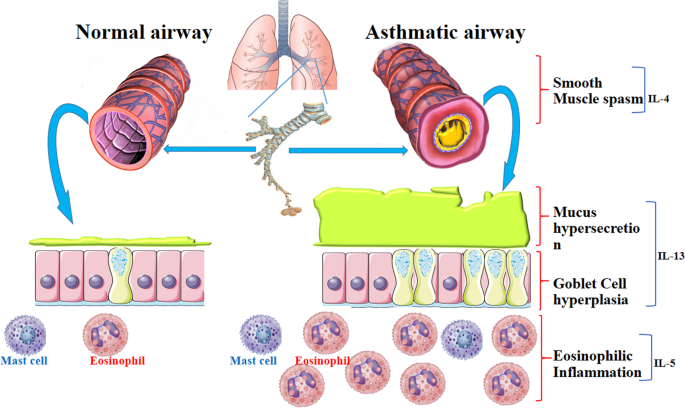
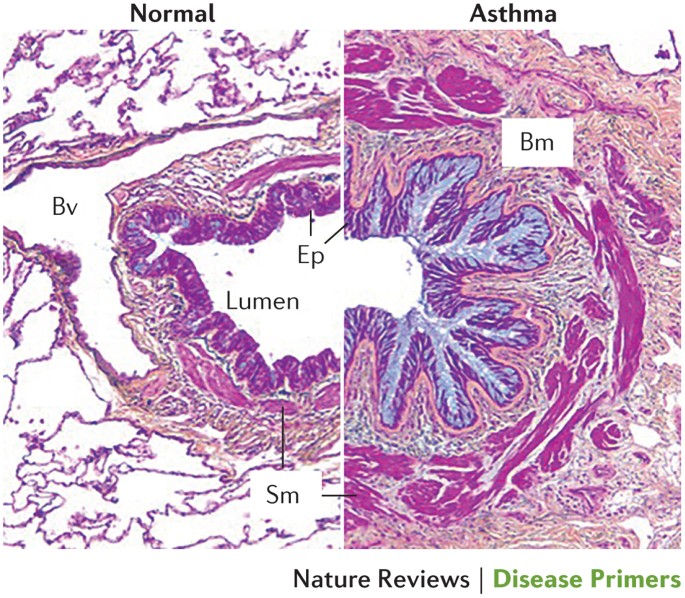
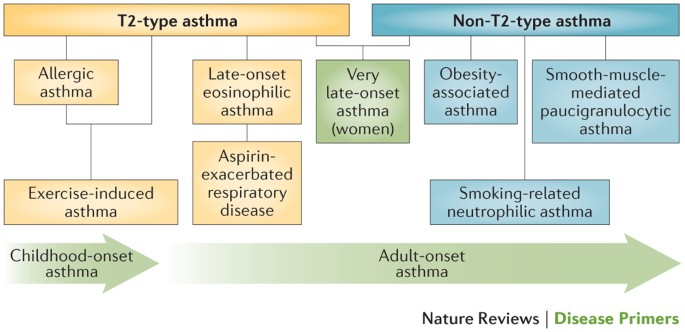
Is asthma an inflammatory disease. Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease involving many different cell types and cellular elements. Although eosinophilia is the most characteristic type of inflammation in asthma this is neither an exclusive feature nor the only type of inflammation observed and eosinophilic asthma is now considered a distinct phenotype of asthma associated pathologically by thickening of the basement membrane and pharmacologically by corticosteroid responsiveness. 6 Inflammation leads to.
It can have positive effects like helping eliminate a parasitic infection. This makes them extra sensitive to things that you are exposed to in the environment every day or asthma triggers. Severe asthma is one form of the disease.
3 Even when you are not experiencing asthma symptoms your airways can still be inflamed. Inflammation is the root of the problem in asthma. 1-3 Approximately 1 in 10 patients with asthma have.
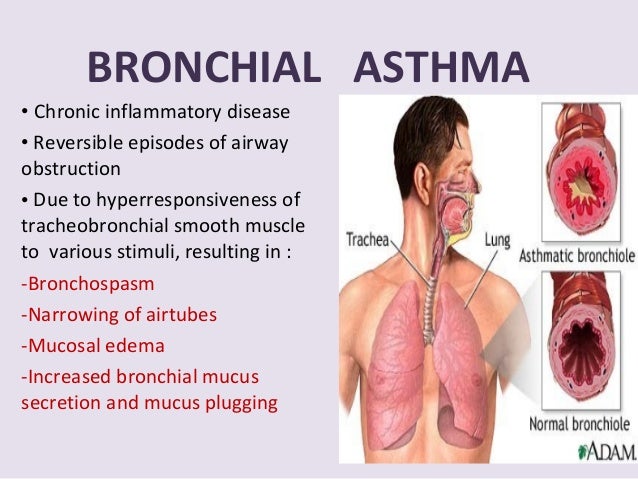
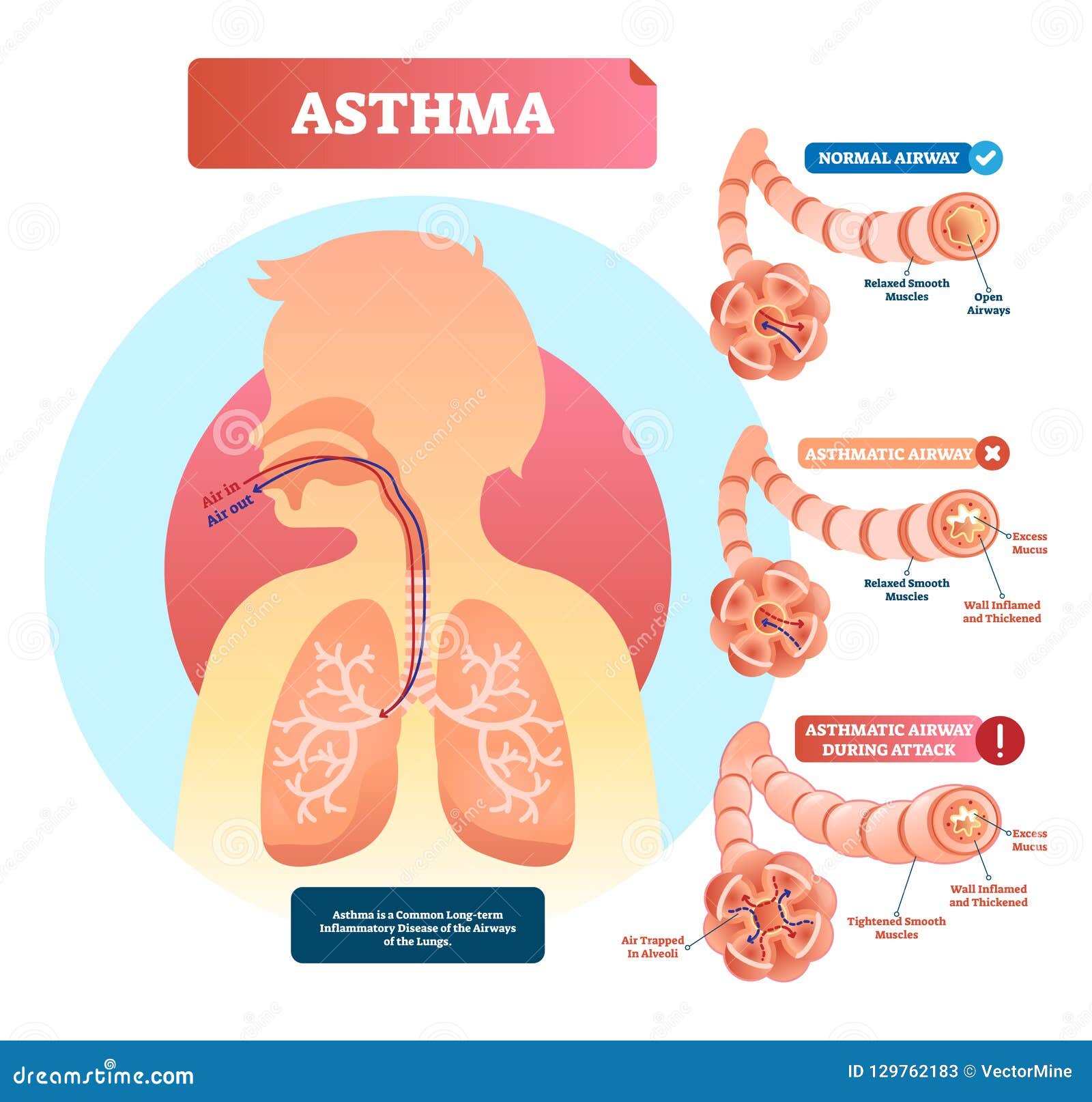
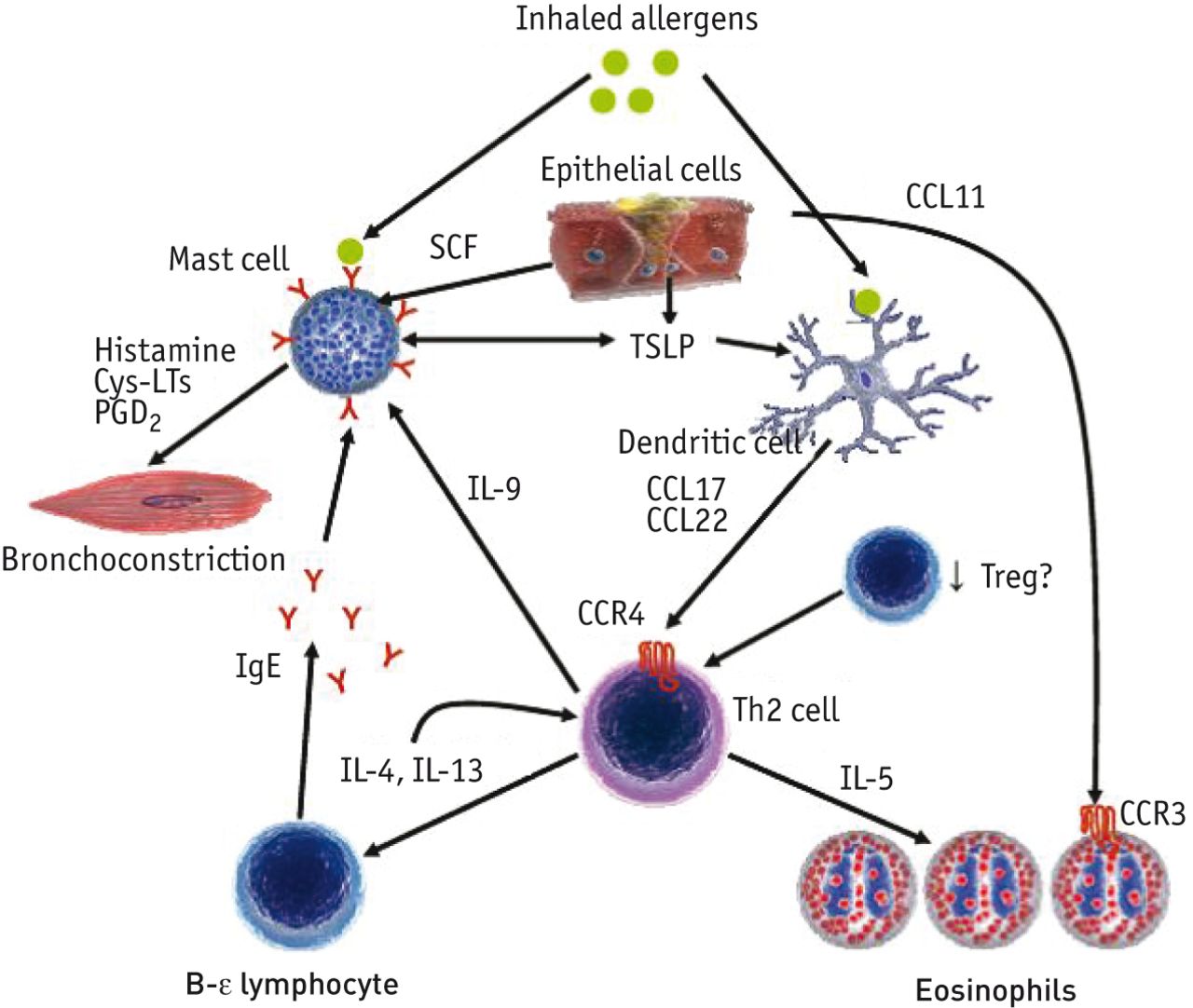
3 Airway sensitivity also called hyperresponsiveness or irritability Limited airflow also called airway obstruction. But it also plays a role in certain medical conditions such as atopic dermatitis eczema allergic rhinosinusitis and some types of asthma. Inflammation and narrowing of the small airways in the lungs cause asthma symptoms which can be any combination of cough wheeze shortness of breath and chest tightness.
Asthma affected an estimated 262 million people in 2019 and caused 461000 deaths 1. Indirect assessment of airway inflammation includes examination of sputum or serum for eosinophils or eosinophil-derived products but examination of bronchial mucosal biopsies. If you have asthma you know that inflammation causes the inner lining of your airways to swell and produce mucus.
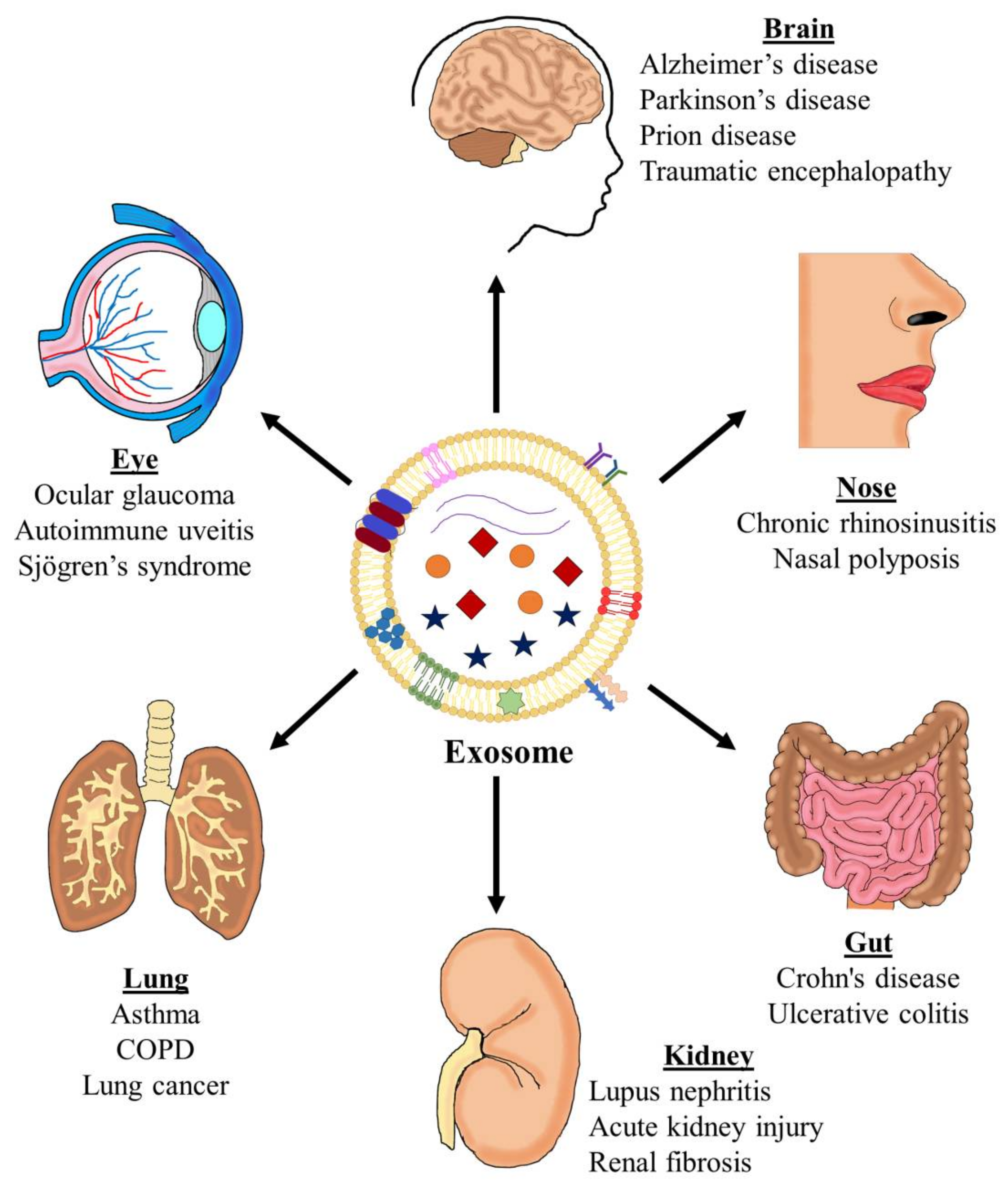
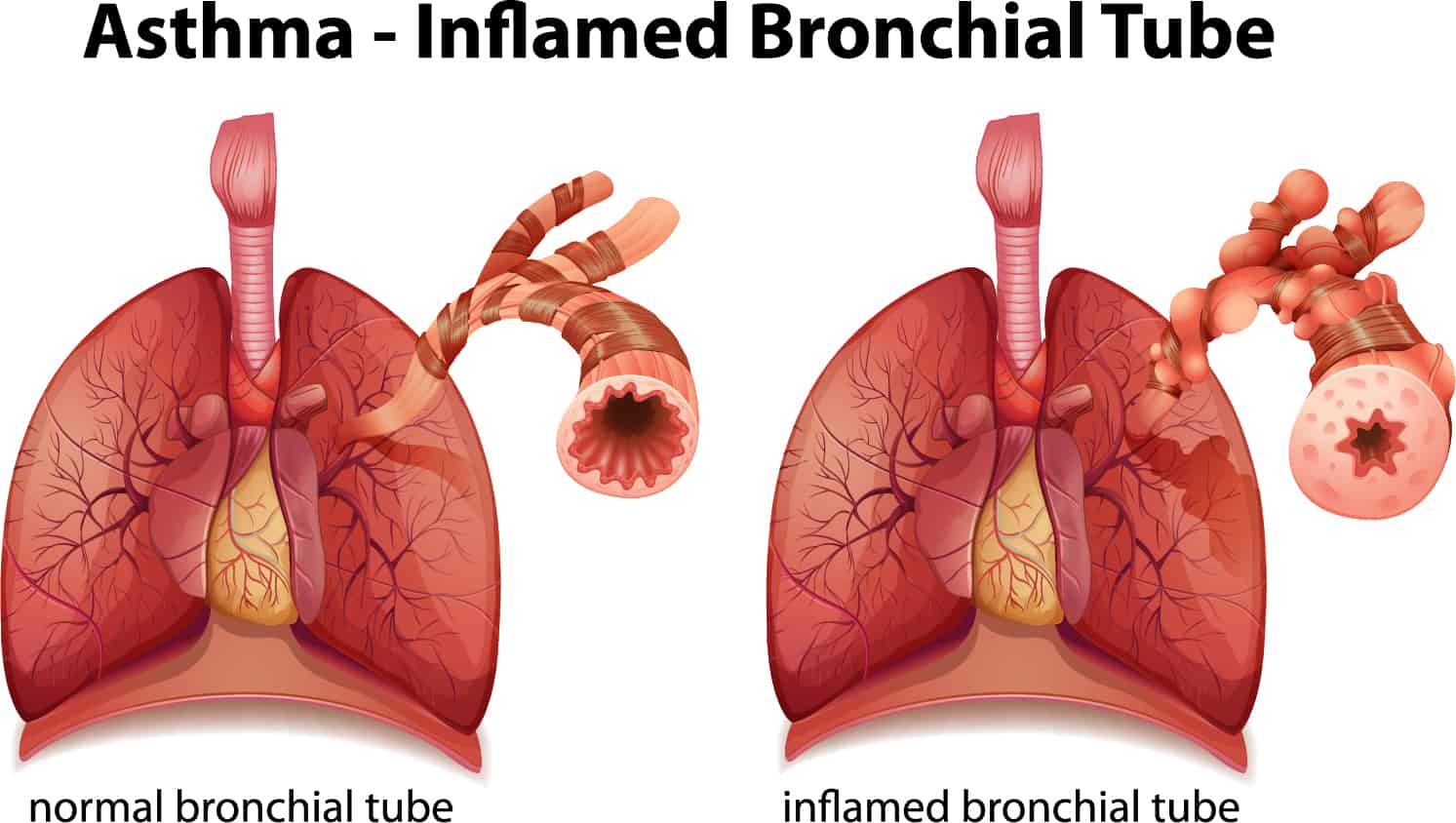
Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the airways to the lungs. This leads to common asthma symptoms. It makes breathing difficult and can make some physical activities challenging or even impossible.
The autoimmune hypothesis is further supported by the response to immunosuppressive drugs. This inflammation makes the airways more sensitive to certain asthma triggers that cause asthma attacks.
It can have positive effects like helping eliminate a parasitic infection.
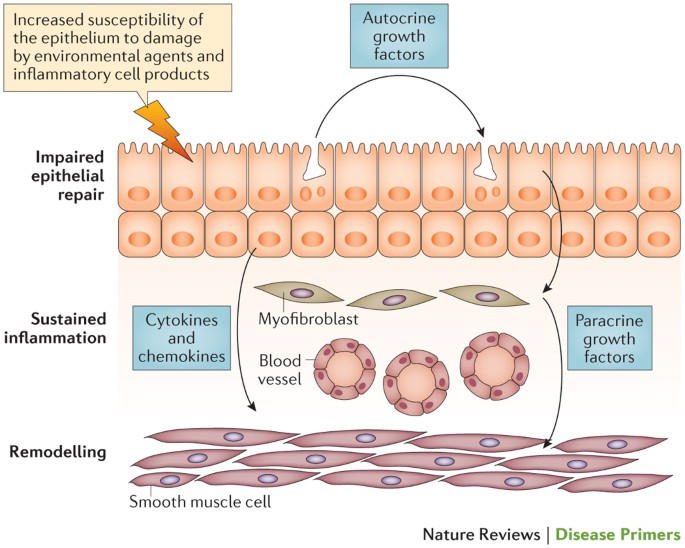
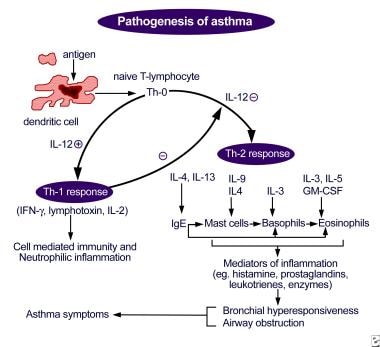
Asthma is characterized by chronic inflammation of the respiratory airways that can be triggered by allergen exposure or by other mechanisms possibly autoreactive autoimmune. The autoimmune hypothesis is further supported by the response to immunosuppressive drugs. 3 Even when you are not experiencing asthma symptoms your airways can still be inflamed. Evidence suggests that in the long term this inflammation leads to remodeling of the airways airflow obstruction and the bronchial hyperreactivity symptoms of asthma and is present even in patients with intermittent disease. Inflammation is the root of the problem in asthma. 3 Airway sensitivity also called hyperresponsiveness or irritability Limited airflow also called airway obstruction. With asthma the airways in your lungs are often swollen or inflamed. Coughing wheezing and shortness of breath. Asthma is a major noncommunicable disease NCD affecting both children and adults.
According to the Centers for. Asthma is an inflammatory disease of the airways to the lungs. Inflammation is the root of the problem in asthma. It can have positive effects like helping eliminate a parasitic infection. Although eosinophilia is the most characteristic type of inflammation in asthma this is neither an exclusive feature nor the only type of inflammation observed and eosinophilic asthma is now considered a distinct phenotype of asthma associated pathologically by thickening of the basement membrane and pharmacologically by corticosteroid responsiveness. If you have asthma you know that inflammation causes the inner lining of your airways to swell and produce mucus. Genetic and environmental factors play a role in airway inflammation and hyper-reactivity.


































Post a Comment for "Is Asthma An Inflammatory Disease"