Maxillary Sinus Fracture Treatment
Maxillary sinus fracture treatment. For example anterior wall of the frontal sinus is usually managed conservatively by contrast posterior wall of frontal sinus require surgery due to potential extension into intracranial space. Conservative management can be an option for maxillary frontal and ethmoid sinus fractures. Your provider will prescribe antibiotics if theres a high risk of infection.
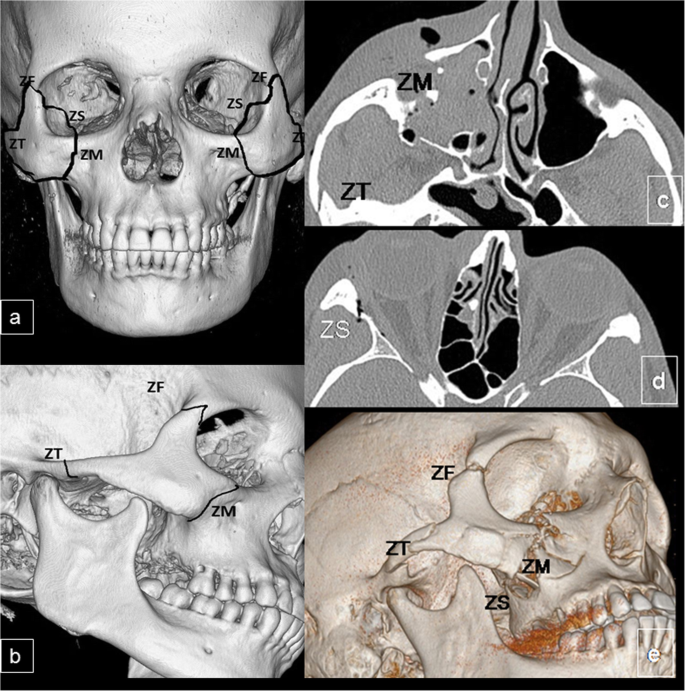
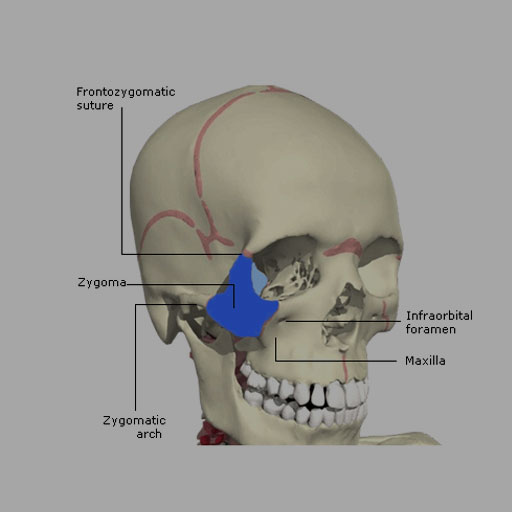
Traditionally the treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis is usually prescription of a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic resistant to beta-lactamase administered for 10 days. The zygoma makes up the lateral. If NOE complex injury is suspected a CT scan with both axial and coronal views is required.
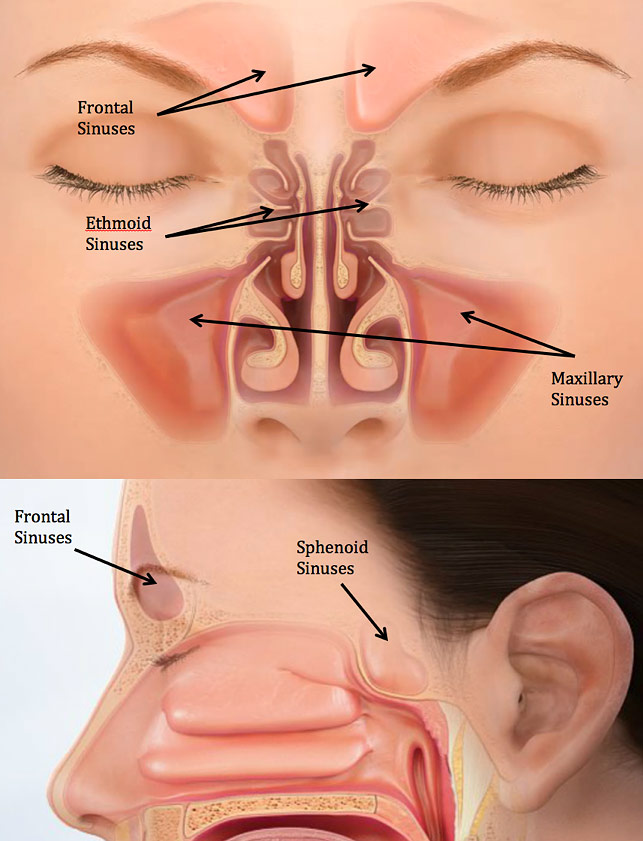
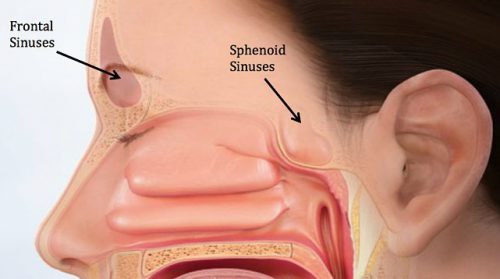
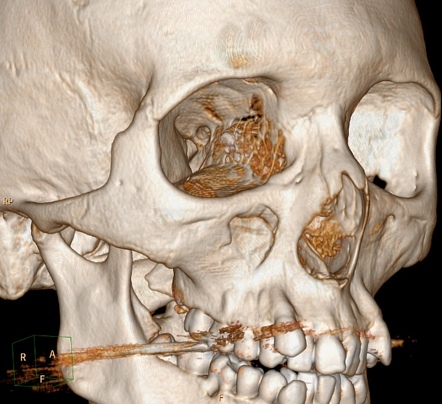
The pyramidal-shaped maxillary sinus is the first sinus to develop embryologically and is the largest of the paranasal sinuses. Numerous methods and mechanical devices have been perfected for the treatment of fractures of the superior maxilla. The patients ranged in age from 10 to 45 years with an average age of 316 years.
Patients with facial fractures involving sinus cavities commonly receive 7 to 10 days of prophylactic antibiotics yet no literature exists to support or refute this practice. Treatment is dictated by the complexity of facial fracture sinus wall location and associated injuries. The treatment of maxillary sinus fractures can require an interprofessional team depending on the extent of the injury.
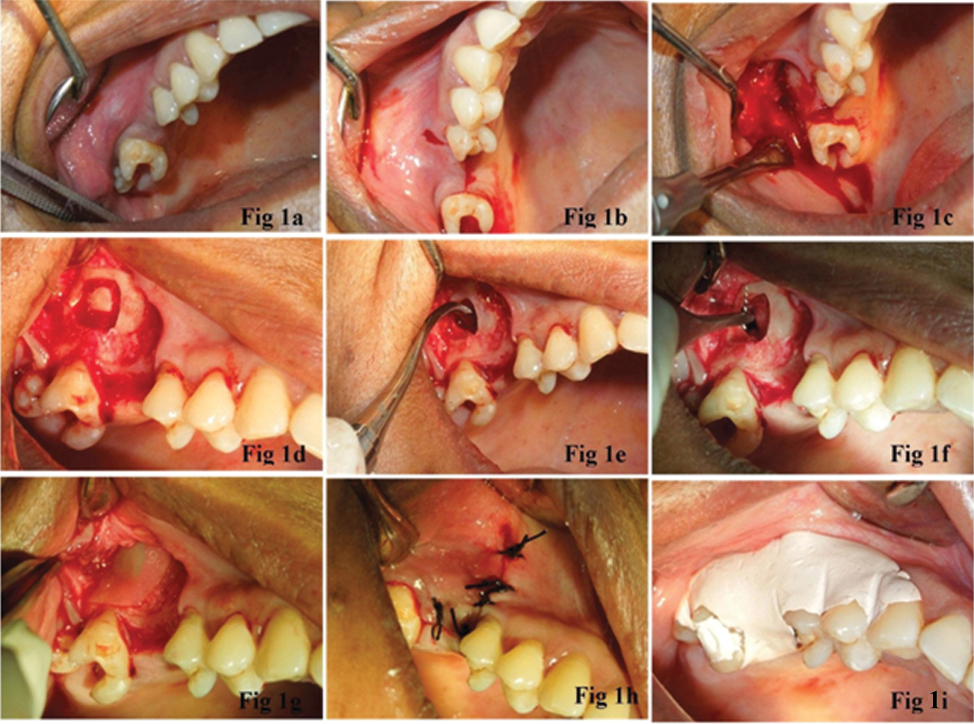
In general fractures may be treated by performing a closed reduction resetting the broken bone or bones without surgery or an open reduction surgery that requires an incision to reposition the fractured bones. Prophylactic antibiotic use for isolated MSFs is still controversial in the literature. Ethmoid sinus fractures are typically not repaired.
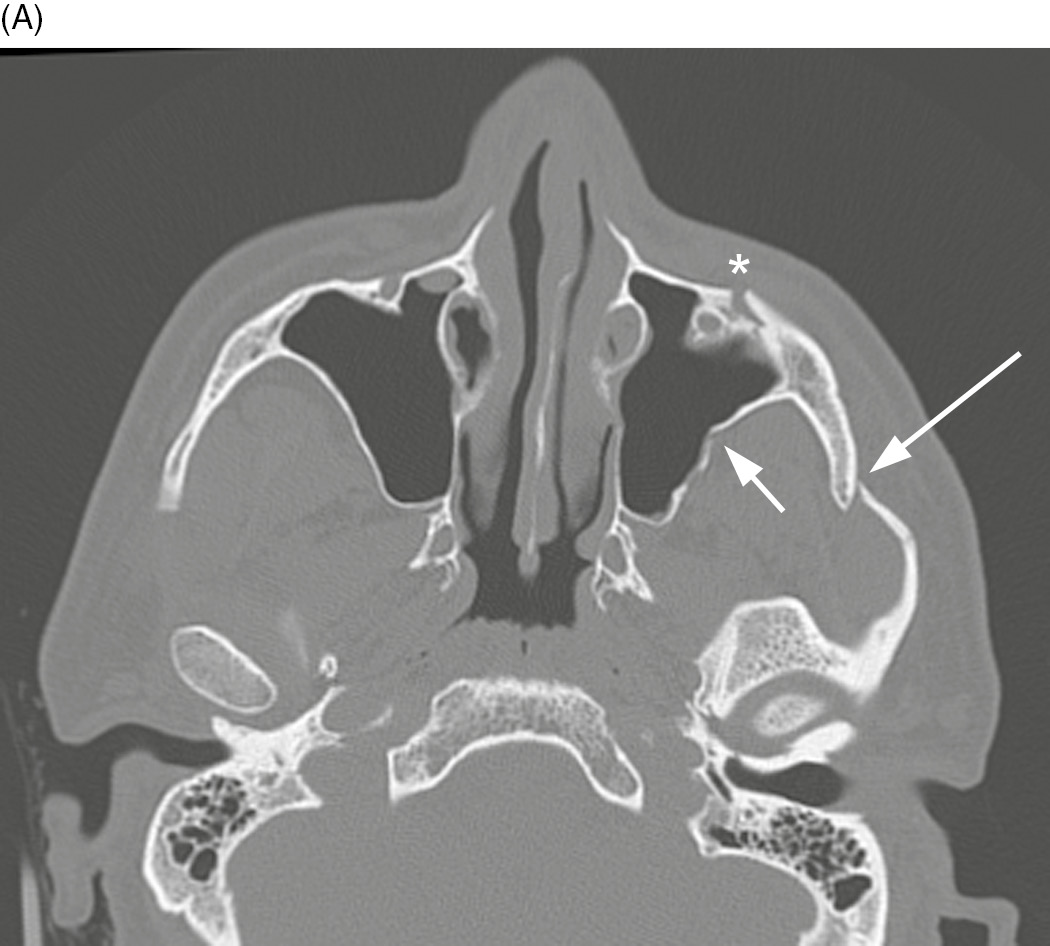
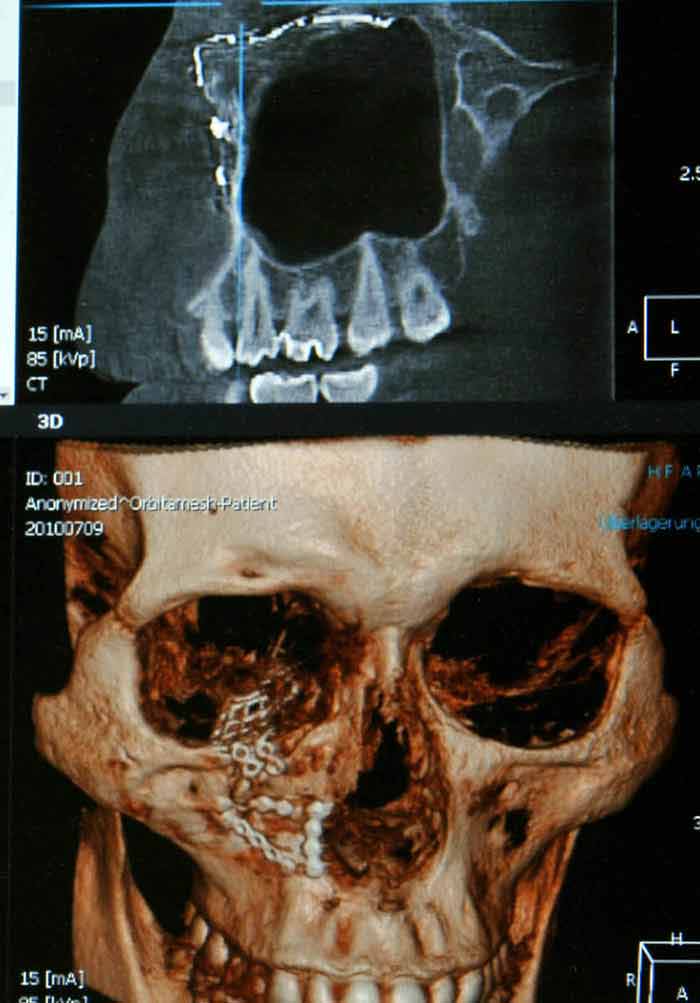
As in the case of The CT scan results revealed Irving sustained a small left Maxillary Fracture. The frontal sinus is not well developed until ages 5-8 years and without the sinus to provide a cushion fractures tend to extend superiorly up. Posteriorly the infratemporal surface of the maxilla makes up the anterior border of the pterygopalatine fossa.
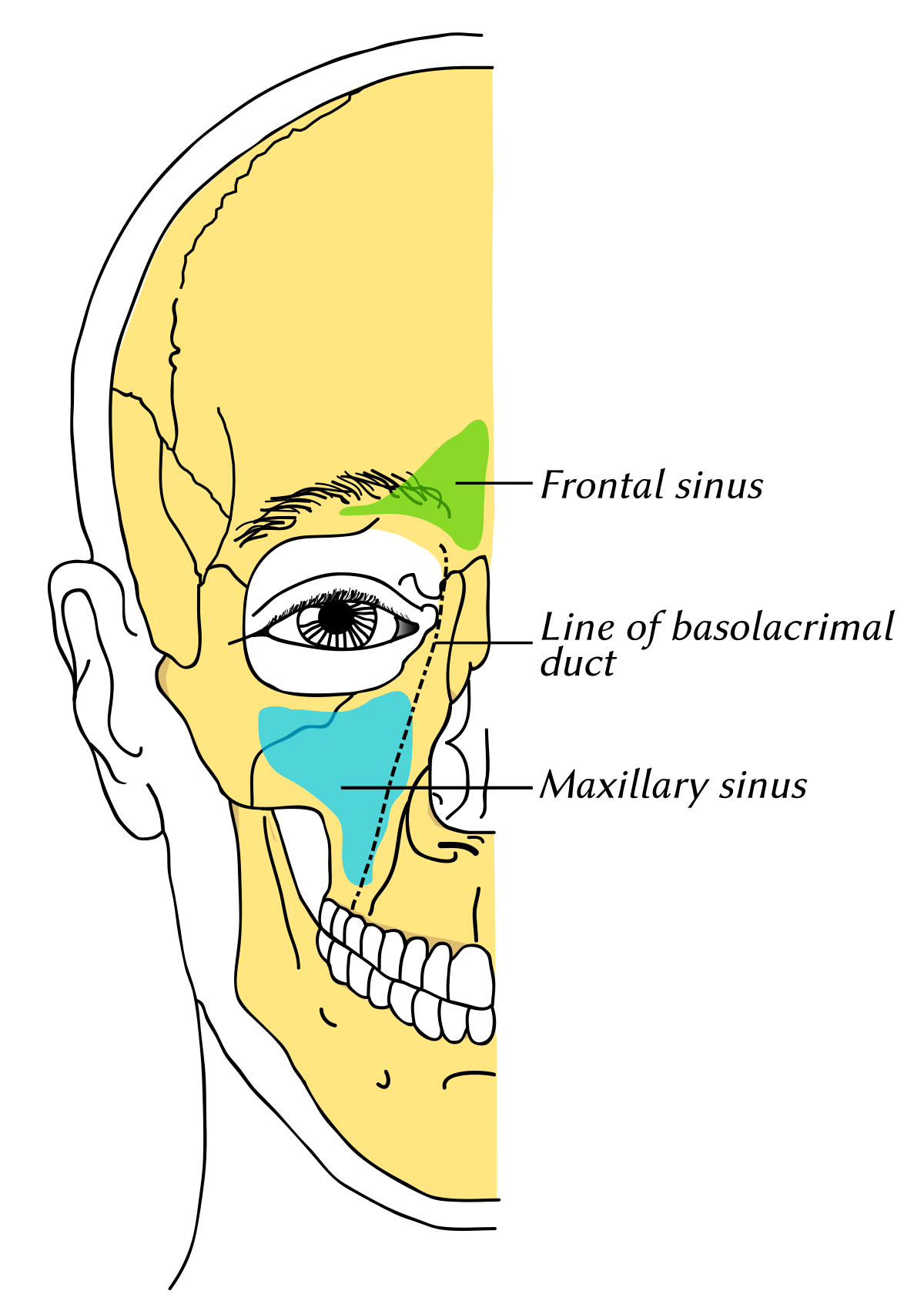
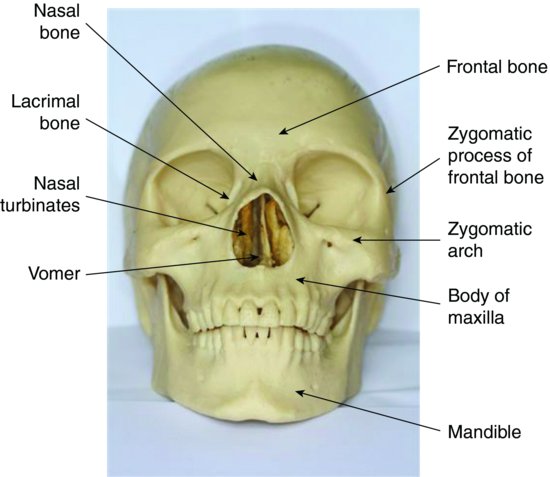
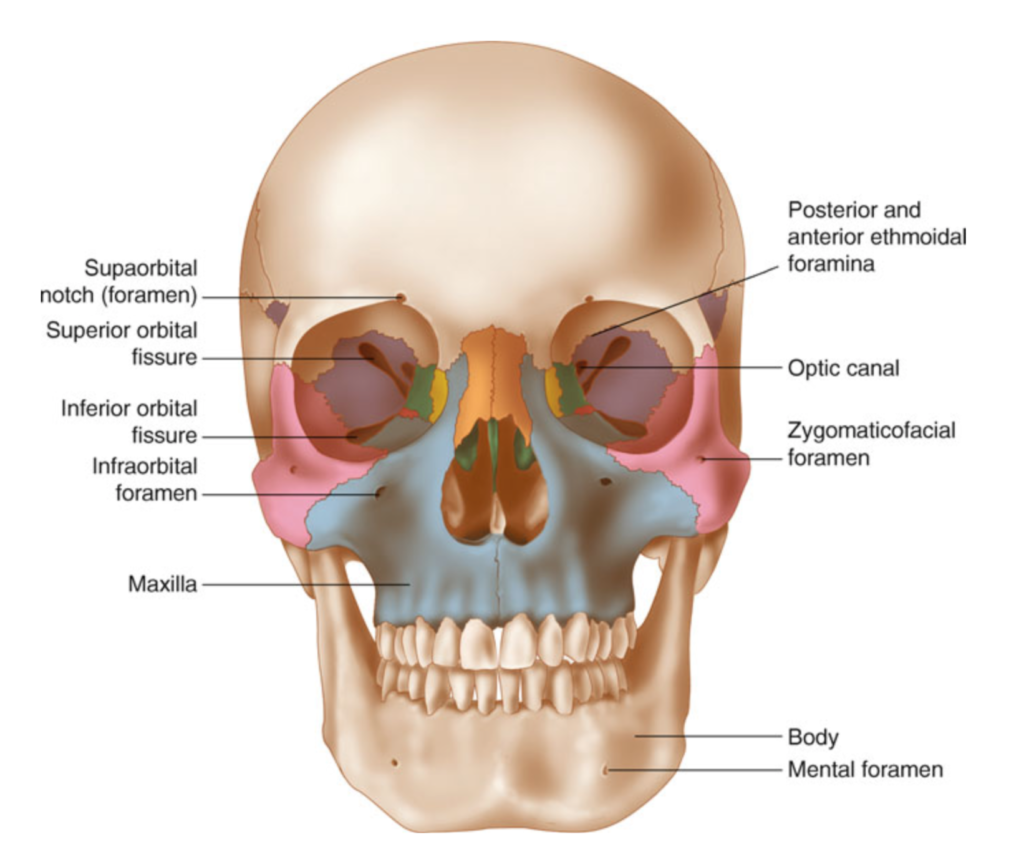
The anterior wall is made up of the bony maxilla. Recent studies have found that the cause of chronic sinus infections lies in the nasal mucus not in the nasal and sinus tissue targeted by standard treatment.
The frontal sinus is not well developed until ages 5-8 years and without the sinus to provide a cushion fractures tend to extend superiorly up.
The floor of the sinus is made up of the alveolar and palatine processes of the maxilla bone. Ethmoid sinus fractures are typically not repaired. Traditionally the treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis is usually prescription of a broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic resistant to beta-lactamase administered for 10 days. Your provider will prescribe antibiotics if theres a high risk of infection. Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes. Numerous methods and mechanical devices have been perfected for the treatment of fractures of the superior maxilla. The patients ranged in age from 10 to 45 years with an average age of 316 years. The need for treatment of an isolated nasal fracture is usually based on clinical evaluation and X-rays are not considered routine unless suspicion of other facial injuries exists. As in the case of The CT scan results revealed Irving sustained a small left Maxillary Fracture.
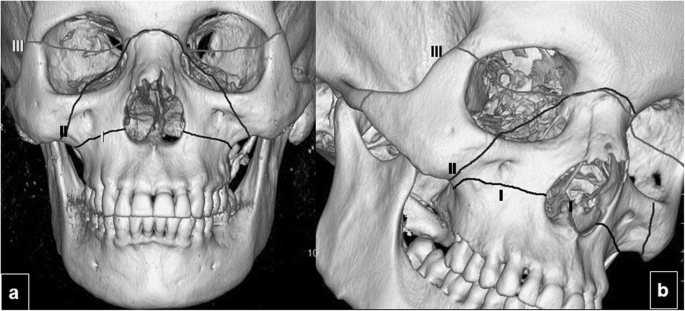
In addition 3-D CT reconstructions may be indicated. Recent studies have found that the cause of chronic sinus infections lies in the nasal mucus not in the nasal and sinus tissue targeted by standard treatment. Crepitation to palpation is indicative of orbital emphysema. 19 Describe the treatment of a severely displaced maxillary fracture in conjunction with a nasoorbitoethmoidal fracture and a mandibular fracture The approach to the maxillary fracture should be via a coronal flap with exposure of the nose as well as the medial and lateral orbital walls. Numerous methods and mechanical devices have been perfected for the treatment of fractures of the superior maxilla. The need for treatment of an isolated nasal fracture is usually based on clinical evaluation and X-rays are not considered routine unless suspicion of other facial injuries exists. The treatment of maxillary sinus fractures can require an interprofessional team depending on the extent of the injury.


























Post a Comment for "Maxillary Sinus Fracture Treatment"